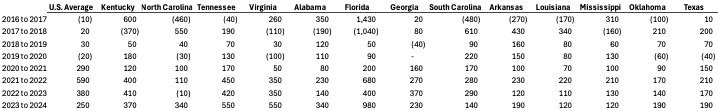
While on the road doing preplant meetings around the country, one of the questions we’ve been asked the most by farmers is: with reduced farm profitability, why haven’t land values declined? Over the past year, there have been two Southern Ag Today articles that have addressed different parts of this issue. Kim discussed the trends in Southern farmland values while Loy and Biram addressed the relative profitability of U.S. farms, looking at the disparity between crop prices received and input prices paid. Table 1 indicates that, while not very often, Southern state cropland values have occasionally decreased (indicated by numbers in parentheses) over the past nine years.
The question of why land values haven’t reacted to reduced profits requires a multifaceted answer that most farmers don’t like to hear. The first part of the answer is that land values should follow farm profitability to a degree, but farm profitability isn’t the only factor. Long-term interest rates – or the cost of borrowing money – also matters. With current interest rates relatively high, there should be downward pressure on farmland prices.
The part of the answer they like the least is also where we tend to get agreement from them: farmers are not the only people trying to buy farmland. During almost every one of our Agricultural and Food Policy Center (AFPC) representative farm updates, the farm panel members talk about how hard it is to buy land at prices that can realistically be paid back with expected farm profits. So, who else is buying land? Nonfarm real estate investors such as publicly traded farmland real estate investment trusts (REITs), insurance companies, and just about anyone who wants to use real estate as an investment are actively investing in farmland across the United States. The two farmland REITs that people talk about the most are Farmland Partners and Gladstone Land. Both REITs own land in multiple states.
Farmland values and agricultural profitability are related, but in today’s farmland markets, there are many other factors and players that influence the value of U.S. farmland.
Table 1. Change in Southern State Cropland Values, Annually from 2016 to 2024.
Outlaw, Joe, and Bart L. Fischer. “Why Haven’t Land Values Reacted to Reduced Farm Profits?” Southern Ag Today 5(7.4). February 13, 2025. Permalink






