According to the most recent estimates from the USDA ERS, the US agricultural sector is projected to experience a significant decline in profitability. Overall, current estimates indicate that net farm income in 2024 will be 6.8% lower than in 2023, a year that already saw a substantial drop compared to 2022. Expected cash receipts are anticipated to decline most sharply for corn, soybean, and cotton producers, with decreases ranging from 14% to 22% relative to last year. This suggests that some commodity producers will face increased financial pressure for the remainder of 2024 and possibly into early 2025.
A recent survey of agricultural bankers supports this observation, indicating rising financial stress among agricultural producers. The Agricultural Credit Survey conducted by the Kansas City Fed reveals that more agricultural lenders are receiving requests for loan renewals and extensions, a sign that producers are struggling to meet loan interest and principal payments. However, beyond these requests, there is currently no clear evidence that financial pressures are translating into widespread farm financial distress. According to the Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED), default rates on agricultural production loans and farmland loans have not shown significant increases in the latest survey.
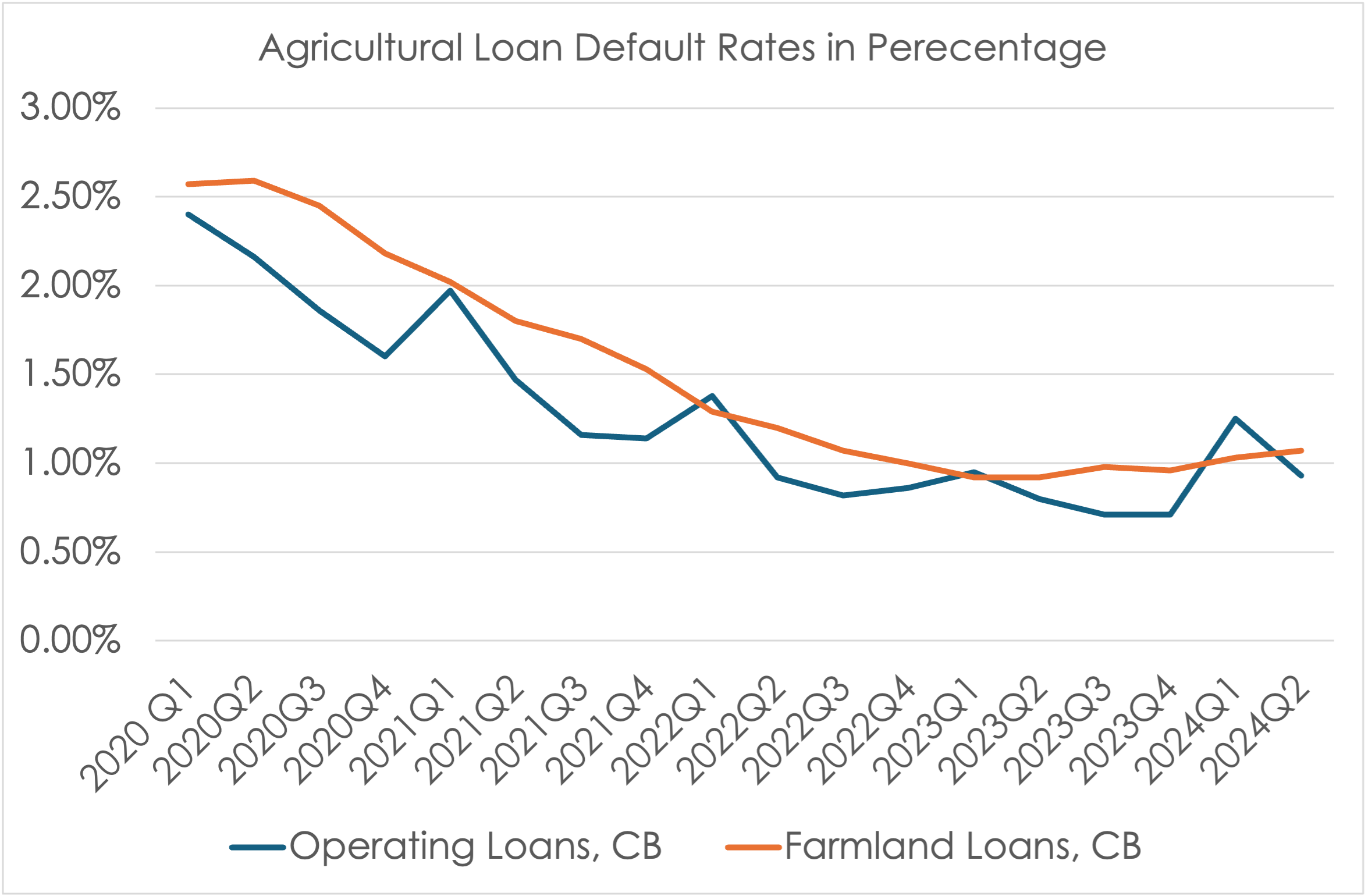
One contributing factor to the pressure felt by both agricultural producers and consumers is the rise in interest rates. Compared to the rates offered from 2020 to 2022, interest rates on farm production loans and farmland loans have increased sharply following a series of rate hikes by the Federal Reserve (the Fed) aimed at curbing rapidly rising inflation. As the Fed raised the federal funds rate—used as a benchmark for determining consumer loan interest rates—farm loan interest rates also rose, leading to greater pressure on repayment schedules. In the most recent survey of bankers in the Kansas City Federal district, the average farm production loan interest rate was 8.83%, and the farmland loan interest rate was 8.04%. In the same quarter of 2021, these rates were about 5.04% and 4.57% respectively. While 2020 or 2021 rates were very favorable rates in comparison to the long-term average, rapidly increasing interest rates in such a short period of time in 2022 could have put extra financial pressure on some producers who were not prepared for such rapid change.
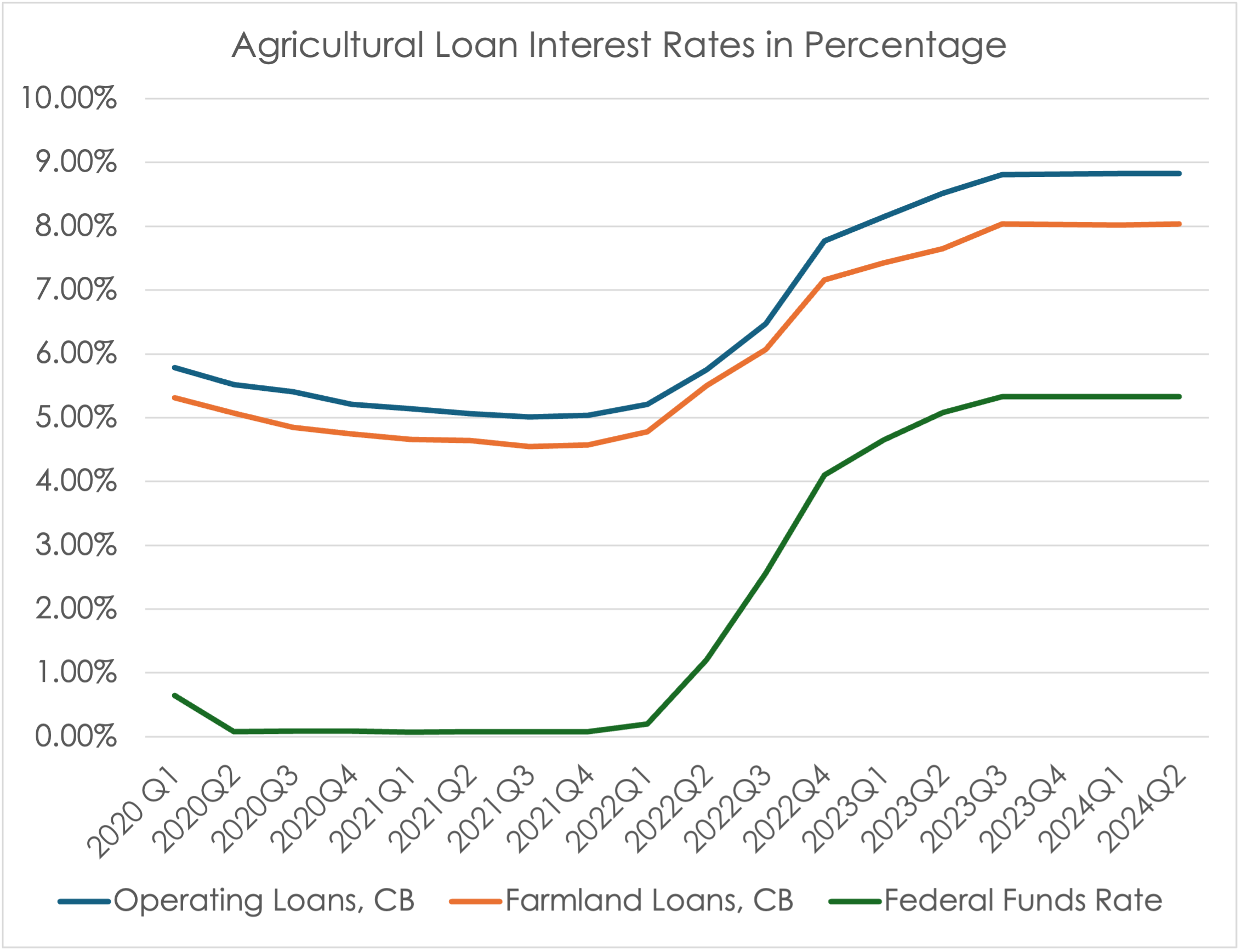
However, as observed in September 2024, multiple reductions in interest rates are expected in the coming months and years. The Fed aims to lower the federal funds rate to 3.5% by the end of 2025 and to 3% by the end of 2026. Given that the pace of these rate reductions is expected to be slower than the hikes experienced in 2022 and 2023, the anticipated decreases in farm loan interest rates are also likely to be gradual.
Kim, Kevin. “2024 Agricultural Lending Condition Update.” Southern Ag Today 4(43.1). October 21, 2024. Permalink

Leave a Reply